Over the years, I’ve watched as SSL / TLS certificate validity periods have steadily shortened, each change pushing us toward stronger security practices. Now, with the Certificate Authority/Browser (CA/B) Forum’s latest decision to reduce certificate lifespans to just 47 days by 2029, we’re standing at the edge of another major shift, one that will dramatically change how we manage and maintain certificates moving forward.
- Understanding the Change
- Timeline and Technical Details
- Business Impact
- Automation and Solutions
- Special Cases and Exemptions
- Strategic Readiness
- Future Proofing
Understanding the Change
What is the 47 Day Certificate Validity Rule?
Right now, public SSL / TLS certificates max out at 398 days. But in April 2025, Apple’s proposal to reduce this gradually down to 47 days was officially adopted by the CA/B Forum, with all four major browser vendors—Apple, Google, Mozilla, and Microsoft—voting in favor.
This also includes a reduction in the Domain Control Validation (DCV) reuse period, which will drop to just 10 days by March 2029. That means organizations will need to validate domains more frequently tightening the timeline across the entire certificate lifecycle.
Why is This Happening?
It might seem like a lot of hassle just to make certificates expire more often, but there’s a solid reason behind this shift. Here’s why it’s happening:
- Reducing the Risk of Compromised Certificates: Longer-lived certificates present a bigger window of vulnerability. If a certificate is compromised, attackers can misuse it for far longer. By shortening certificate validity, the risk of these long-lived certificates being exploited is drastically reduced.
- Pushing for Automation: The new rule is also a big nudge toward automation. With certificates expiring so frequently, manual renewals just aren’t going to cut it anymore. This is the CA/B Forum’s way of driving the industry toward more efficient, automated workflows that reduce human error and improve overall security.
- Keeping Systems Agile: In the event of a breach or other security concerns, you want your system to respond quickly. Shorter lifespans mean that compromised certificates are cycled out faster, improving the agility of your security posture and minimizing damage.
- Getting Ready for a Post-Quantum World: Another reason for the shorter validity periods? The world of cryptography is evolving. With quantum computing on the horizon, we're going to need systems that can rapidly adapt. Frequent renewals give us the flexibility to quickly roll out updates—especially as we prepare for post-quantum cryptography.
Essentially, these changes are all about tightening security and paving the way for automation. While it may feel like a headache for IT teams, the Forum believes that the changes will be a net benefit for internet security and safety.
Timeline and Technical Details
What is the Timeline for the Decrease in SSL/TLS Validity Changes?
The dates for implementation are as follows: 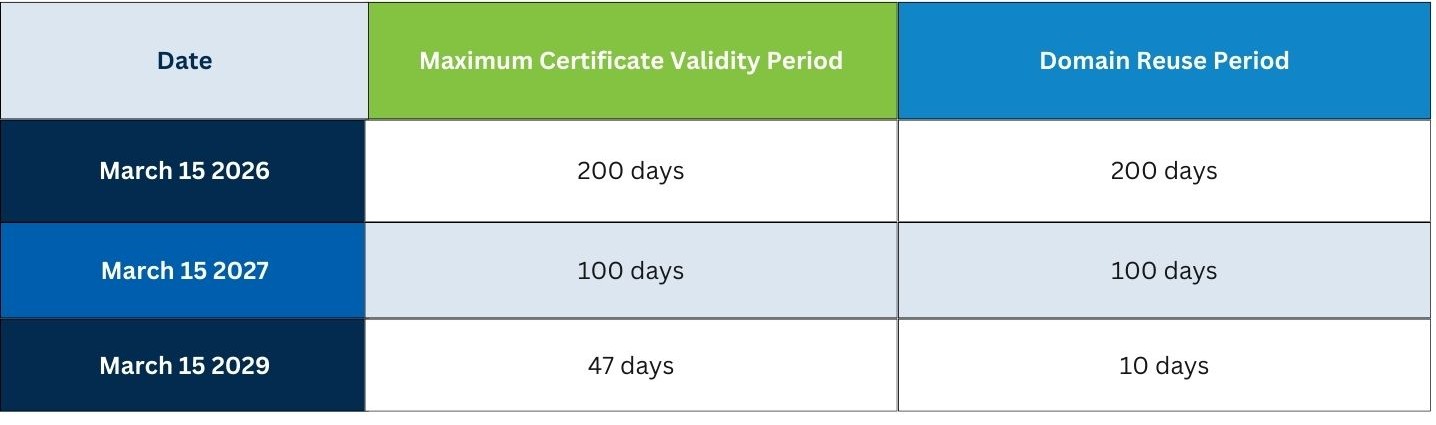
What’s the Difference Between Certificate Lifetime and Domain Validation Reuse?
At first glance, these terms can seem a bit technical, but they’re actually pretty straightforward once you break them down:
- Certificate Lifetime refers to how long an SSL/TLS certificate is valid after it’s issued. Right now, certificates can last up to 398 days, but with the upcoming changes, they’ll expire much sooner, down to just 47 days by 2029.
- Domain Validation Reuse is about how long a Certificate Authority (CA) can use the same proof that you own or control a domain before it needs to verify it again. Currently, the reuse period can be up to 398 days, but by 2029, that will shrink to just 10 days.
To put it more simply:
- The certificate lifetime is about how long your certificate itself is valid.
- Domain validation reuse is about how long the CA can rely on your proof of domain ownership before asking you to confirm it again.
By 2029, the 47-day certificate lifespan will mean that your certificate will expire faster, and with the 10-day domain validation reuse period, you’ll need to validate your domain much more often. This is where automation really starts to come into play, doing it manually just won’t be feasible anymore.
Business Impact
How Will This Affect my Organization?
If you manage certificates today, you know this shift isn’t just about security—it creates real operational challenges. The bottom line? Shorter certificate lifespans mean more frequent renewals, and if your team is still managing certs manually, you’re in for a tough time.
Talk through your challenges with our team today
The reduction of SSL / TLS certificate validity periods from 398 days to 47 days has several significant implications for web security:
- Reduced attack surface: Shorter lifespans mean less time for compromised certificates to be exploited.
- Improved security posture: Frequent renewals ensure certificates use the latest standards and configurations.
- Supports zero-trust principles: Regular renewals ensure trust is continuously validated.
But the operational impact can’t be ignored. While the security benefits of shorter certificate validity periods are the main driver for this shift, they also present significant operational challenges.
- More frequent renewals: Tracking and renewing certs every 47 days isn’t feasible without automation.
- Risk of human error: Manual processes are prone to missed renewals, outages, and compliance gaps.
- Higher resource demand: IT teams may need to allocate more staff, training, or tools to keep up.
- Impact across all businesses: Whether you're a large enterprise or a Small Medium Business (SMB), managing this shift requires a scalable approach.
What Industries are Most Affected?
The short answer? Pretty much every industry that uses SSL/TLS certificates! But some sectors will feel the impact more directly than others, especially those with high-volume, security-sensitive environments. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Finance: Banks, payment processors, and other financial institutions rely heavily on secure transactions, so frequent certificate renewals are crucial to keep everything safe and compliant.
- Healthcare: With privacy regulations like HIPAA in place, healthcare providers need to ensure their systems are always secure. Shorter certificate lifespans will mean more frequent validation to protect patient data.
- Retail and E-commerce: Online stores and marketplaces handle a lot of customer data and payment info, which makes secure certificate management a priority for avoiding fraud and maintaining trust.
- Government and Public Services: Government agencies are high-profile targets for cyber threats, so frequent certificate updates will help keep sensitive information secure and maintain public trust.
- SaaS and Cloud Providers: These businesses often handle large amounts of data for their clients. Shorter certificate lifespans mean better security for both the provider and their customers.
Of course, every business that uses SSL/TLS certificates to secure websites, applications, or any digital communication will be impacted. Whether you're a global enterprise or a small local shop, shorter certificate lifespans will affect how you manage and renew your certificates.
Automation and Solutions
What Are My Options for Automation?
Your infrastructure, team size, and certificate volumes will shape the right solution for you.
- ACME: If you're looking for a free and easy way to automate domain validation (DV) certificates, ACME is a solid choice. It's a great starting point for businesses that need basic automation without a lot of complexity.
- Certificate Automation Manager: For larger businesses or those with complex infrastructure, this enterprise-grade solution offers full automation capabilities, including renewal management and reporting. It's especially useful for organizations managing multiple domains across different environments.
- Internal PKI: If you have specific needs for non-public-facing systems, setting up an internal PKI with custom rules can give you more control over certificate management. This is ideal for businesses that want to handle their internal certificates in a highly tailored way.
Regardless of where you’re starting, the goal is the same: act now to reduce risk, avoid outages, and get ahead of the curve before the 47 day requirement becomes the norm.
How Do I Implement Automation?
First step? Start by looking at what you already have in place, then build from there.
If you're just beginning, tools like ACME can help automate the issuance and renewal of DV certificates quickly and for free. It's a great first step for teams looking to move away from manual tracking and spreadsheets.
For more advanced needs - like managing multiple certificate types, environments, or teams - you might want to explore a Managed PKI platform or a solution like Certificate Automation Manager. These give you more visibility, policy control, and reporting features, which are especially helpful in larger or regulated environments.
Not sure what you need? That’s okay. Contact GlobalSign for a no obligation review to discuss your requirements and understand what solution is best suited for your needs.
Special Cases and Exemptions
What About OV and EV Certificates?
OV (Organization Validated) and EV (Extended Validation) certificates are a bit different from standard DV (Domain Validated) certificates, but the new rules still apply to them, with a few key points to keep in mind:
- Domain Control Validation: Like DV certificates, OV and EV certificates will follow the same schedule for domain validation reuse. That means, by 2029, domain validation will need to be rechecked every 10 days.
- Subject Identity Information (SII): For OV and EV certificates, the organization’s identity information (like business name and address) must still be revalidated annually. This is a manual step, but it ensures that the certificate reflects the current and accurate information about the organization requesting it.
- Manual Verification: OV and EV certificates often require more detailed checks, like phone calls or other methods of verification, which will remain part of the process even as certificate lifespans shrink.
While OV and EV certificates will have the same domain validation timing as DV, the process still involves some extra steps to verify the organization's identity. This means more frequent checks, but with the added assurance that the identity of the organization is carefully validated.
Will Browsers Reject Longer Certificates After the Rule Changes?
No, browsers won’t suddenly stop trusting certificates that were issued before the new rules take effect.
The upcoming changes apply to certificate issuance, not validation. That means if you get a 398 day certificate before the cutoff (before March 15, 2026), browsers will continue to trust it until it naturally expires, even if that’s after the new limits kick in.
So, nothing will break overnight. But once the new dates hit, any new certificates issued will have to follow the shorter validity periods. It's a good idea to plan ahead and start adjusting your processes now.
Are Internal PKIs Affected?
No, internal PKIs aren’t covered by the CA/B Forum rules.
These changes only apply to public SSL / TLS certificates issued by publicly trusted Certificate Authorities. If you're using an internal PKI for things like internal apps, dev environments, or non-public systems, you're free to set your own certificate lifespans and validation policies.
That said, this could still be a good time to re-evaluate your internal PKI strategy. Aligning internal practices with the new standards, like using shorter lifespans and adding automation, can improve consistency, reduce risk, and make it easier to manage certificates across your entire environment.
Strategic Readiness
What Should We Do Now?
2029 might seem a long way off, but there are important changes coming well before then. Being proactive now will help you avoid costly outages or last-minute scrambles.
It’s not just about shorter validity—it’s about modernizing how you manage certificates overall. Here’s how to start:
1. Get Visibility with a Certificate Inventory Audit
Make sure you know where all your certificates are. Gaps in your inventory create risk. Tools like Atlas Discovery can help provide a clear view of your certificate landscape.
2. Define Certificate Policies and Workflows
If you haven’t already, create a centralized policy that covers certificate issuance, renewal, revocation, and access control. Standardizing workflows helps teams coordinate and reduces inconsistencies across environments.
3. Adopt Automation Based on Your Needs
Look at what your infrastructure can support today, and what you'll need as certificate volumes grow. Whether you’re starting with ACME or moving toward a fully managed Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) solution, automation is essential for staying on top of renewals.
⚠️ Just a note: ACME is a great start for automating SSL / TLS issuance and renewal, but it’s not a complete lifecycle management solution. If you need end-to-end visibility, reporting, and policy enforcement, you’ll want a more advanced tool.
4. Monitor and Report Continuously
Use monitoring and alerting to stay ahead of expiring certificates and policy violations. Reporting is also key for audits, ISO compliance, and internal accountability.
5. Train Your Teams
Make sure your team understands the upcoming changes, and the tools and processes in place to support them. Awareness reduces errors—and helps everyone move faster.
Can I Still Get a 398 Day Certificate Before 2026?
Yes, you still have time.
If you renew or purchase a certificate before March 15, 2026, you can still get the current maximum validity of 398 days. After that date, new certificates will follow the shorter lifespans set by the CA/B Forum’s timeline, starting with a 200 day maximum.
So if you’re looking to get the most out of your next renewal, now’s the time to plan ahead. Just keep in mind: shorter lifespans are coming, and automation will soon be a must.
Future Proofing
Is This Related to Quantum Computing?
Not directly, but it’s part of the bigger picture.
Shorter certificate lifespans help prepare the internet for post-quantum cryptography (PQC), new encryption standards designed to protect against future quantum threats. When those new algorithms roll out, certificates may need to be updated more frequently.
By shortening lifespans now and encouraging automation, the industry is getting ahead of that shift and building more flexible, future-ready infrastructure.
How Do Non-Browser Clients (VPNs, IoT) Adapt?
Great question, browsers aren’t the only systems that rely on certificates. Many non-browser clients, like VPNs, IoT devices, internal apps, and legacy systems, also depend on SSL/TLS to establish secure connections. So how do they keep up with shorter certificate lifespans?
- Some support automation already: Many modern systems, including some VPN appliances and IoT platforms, support protocols like ACME, which makes it easier to automate certificate issuance and renewal, just like you would for a website.
- Others may need custom solutions: For systems that don’t support automation out of the box, you might need to build or script your own workflows to handle renewals, installation, and validation. That could involve using APIs, scheduled tasks, or integrating with internal tools.
- Start with an inventory: Before making any changes, it’s a good idea to audit your environment and identify which systems are using certificates, how they’re configured, and whether they can be automated. This helps avoid surprises later and ensures nothing gets missed.
Non-browser clients won’t be left behind, but they may require a bit more hands-on planning. With the right strategy in place, you can bring these systems into your automation plan and keep everything running smoothly.
Being Ready for the Shift
Managing certificates doesn’t need to be a headache. Whether you’re looking to audit your current inventory, automate renewals, or deploy a full lifecycle management solution, we’re here to help.
Editor’s Note: This blog was originally published on October 16th 2024 but has since been updated to reflect industry changes and new insights.








