The revised Payment Service Directive, most often referred to by its acronym PSD2 officially went into effect in September 2019 – although the European Banking Authority has given companies an extension to achieve strong customer authentication (SCA). That’s good news for most financial institutions because there’s a lot to understand – and do – as a result of the requirements outlined in PSD2.
If you don’t already know, the directive applies to all member states of the European Union (EU) and requires all financial institutions to open their customer information and payment networks to Payment Service Providers (PSPs) and other Third Party Providers (TPPs). The goal of the directive is to remove the monopoly financial institutions have on their users’ data, increase competition, and encourage new, innovative financial solutions, while at the same time establishing standards to ensure interoperability and the security of user data.
Why does the EU get involved in payment traffic?
The PSD2 is the second installment of an already existing payment service directive from 2007. It aims to tackle fraud and malicious activities and increase security for online payments. It also aims to encourage open banking and create more competition. There have been numerous initiatives in recent years to support the use of digital documents and improve digital security. The continuous rise of financial technology companies (known as FinTechs) is testament to this.
What is the RTS SCA/CSC for PSD2?
The Regulatory Technical Standards (RTS) for Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) and Common and Secure Open Standards of Communication (CSC) detail the specific security measures and implementation requirements that financial institutions and TPPs must meet to comply with PSD2.
A core principle of the RTS is common and secure communication between all parties involved. All transactions between payment service providers and financial institutions must take place over secured channels and ensure authenticity and integrity of the data.
What is the role of Qualified Certificates in PSD2?
The RTS specifies two main requirements that involve the use of certificates:
- Payment service provider identification (article 34 of RTS) – PSPs need to identify themselves towards the financial institution’s API. The RTS specifically requires the use of a Qualified Website Authentication Certificate (QWAC) or Qualified Electronic Seal Certificate (QSealC) for this purpose.
- Secure encryption must be applied between all communicating parties (article 35 of RTS) – The RTS does not specify the use of QWACs here, only mandating the use of “strong and widely recognized encryption techniques,” but QWAC’s use of SSL/TLS protocols meet this need.
What type of qualified certificate(s) do I need?
In order to meet both of the above requirements, the EBA (European Banking Authority) recommends the use of QWACs and QSealCs.
QWACs are essentially qualified SSL/TLS certificates. They are used to identify end points, like banks and third-party providers, and they encrypt and protect data during transmission.
QSealCs, on the other hand, protect data and documents from tampering and identify the origin of the data.
Using both types of certificates is ideal because it ensures:
- PSPs are able to identify themselves towards financial institutions. Both QWAC and QSealC authenticate the parties using the certificates.
- Confidentiality and integrity for communications between all parties. QWAC uses SSL/TLS to encrypt sessions and protect data in transit.
- All data actually came from the PSP identified in the certificate. QSealC identifies where the data came from and protects it from tampering.
The table below from PRETA Open Banking Europe provides a great overview and comparison of when and why to use each, further illustrating the benefit of using both in parallel.

How do qualified certificates for PSD2 differ from “regular” qualified certificates
QWACs and QSealCs fall into the category of qualified electronic certificates. In addition to the usual certificate fields, like O for Organisation, OU for Organisation Unit, and C for Country, they also include three extra fields:
• The authorization number of the TPP
• The PSD2 role or roles of the TPP
• The name of the National Competent Authority
How does it work?
It all sounds very complicated – the PSD2 legislation not only comes with a great deal of acronyms and abbreviations but many different parties are involved, too.
We’ve created this graphic below to help visualize the process:
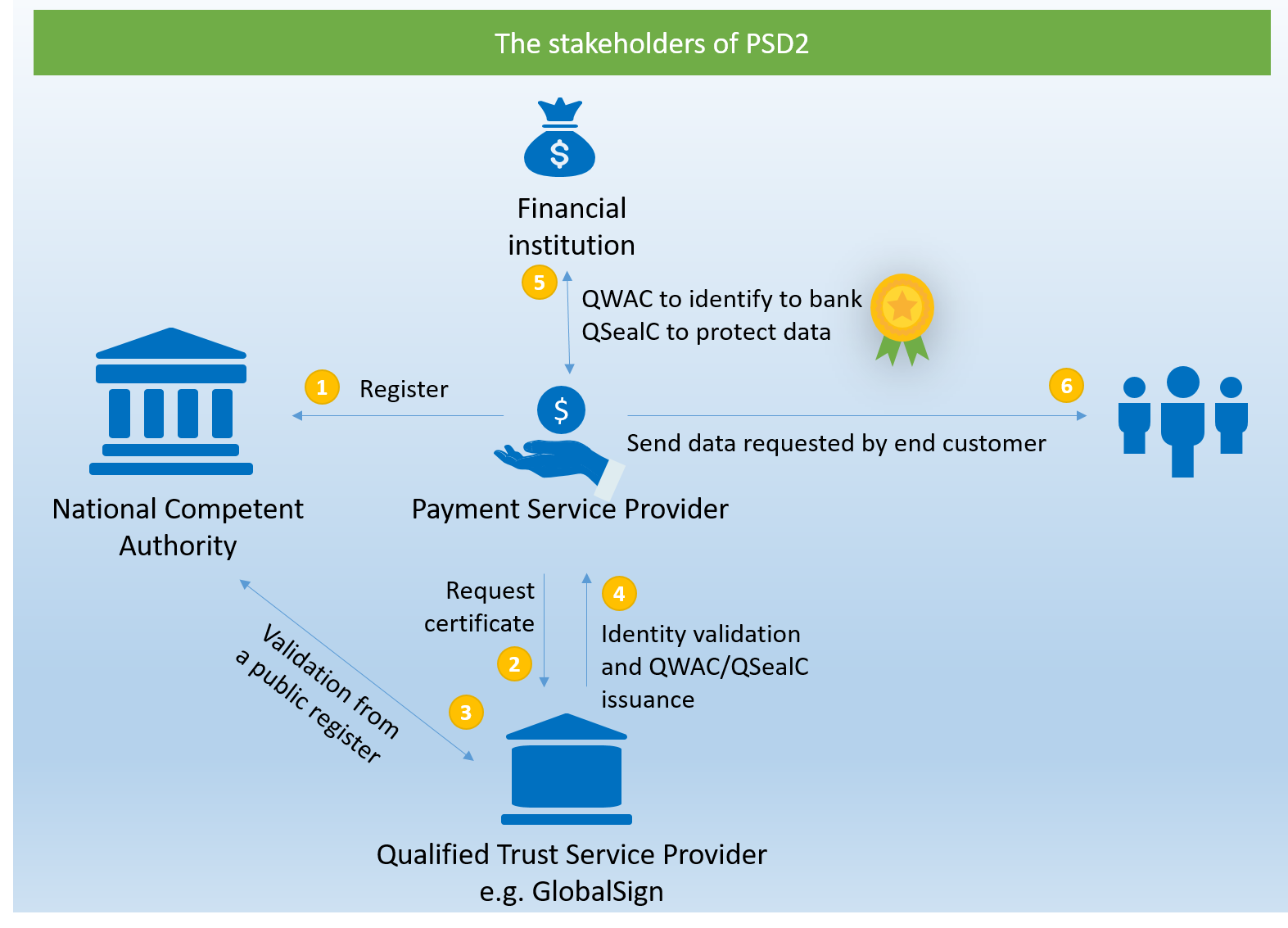
- First, the PSP must register with its respective National Competent Authority.
- It will then approach a QTSP, like GlobalSign, to request a qualified certificate.
- GlobalSign uses the public register that the National Competent Authority creates to validate the Payment Service Provider and issues the QWAC and/or QSealC to the PSP.
- The PSP uses the financial institution’s API(s) to access customer info and payment networks. QWACs and QSealCs are used to identify the PSP, encrypt all communications between the PSP and customer, and protect data from tampering.
- When an end customer requests data, the data gets sent securely from the financial institution via the PSP to the end customer.
What does this mean for banks?
Financial institutions have been tasked with enabling open banking as soon as December 31, 2020 – while that date may seem far off, it’s best to start the process of getting the correct qualified certificates in place now. Any third-party provider that wants access to data needs to be registered with, and approved by, their relevant National Competent Authority (NCA). Based on a successful license, they can then purchase QWACs and QSeals, and in turn request access to financial institution APIs.
How can I get a QWAC or QSealC for PSD2?
These certificates are available from QTSPs like GlobalSign. PSPs and other Third Party Providers (TPP) are welcome to purchase them once they have been vetted and approved by the responsible National Competent Authority.
If you are a PSP and require a QWAC or QSealC, we can help you. Head over to our dedicated PSD2 webpage and learn more about the certificates and how to purchase them.







