What is IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a system of connected objects or “things” that contain sensors, software, and other technologies capable of exchanging data with other objects. They are usually referred to as “smart” devices.
TechTarget also describes the Internet of Things as “a system of interrelated computing devices, mechanical and digital machines, objects, animals or people that are provided with unique identifiers (UIDs) and the ability to transfer data over a network without requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction.”
While not all IoT devices require an internet connection to work, they do require a network connection to automate some operations, issue commands, or update their setup.
IoT in Singapore
In Singapore, both the private sector and the government are starting to outline their approach to IoT.
The Singapore government has already established an IoT technical committee to develop IoT foundational standards in the architecture, interoperability, security, and data protection industries.
In March 2017, the Open Connectivity Foundation (OCF), a leading IoT standards body, collaborated with the Singapore Semiconductor Industry Association (SSIA) to allow IoT devices to seamlessly communicate with one another regardless of manufacturer, operating system, and chipset of physical transport. The collaboration allowed SMEs and startups in the Singapore Smart Nation ecosystem to understand and adopt the specification in their design strategies.
As of today, five IoT standards have been published by Singapore’s Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) together with Information Technology Support Center (ITSC)’s Technical Committee. These IoT standards serve as a guide to create an ecosystem of interoperable sensor network devices and systems. They guide the application, development, and deployment of these devices for public areas, multiple industries, and homes in Singapore.
Of course, as security plays a big part in the IoT ecosystem, guidelines for IoT security for a smart nation have also been established.
How IoT Works
Now that we know what the “things” in the internet of things refer to and how they are interconnected, how do IoT devices work?
Essentially, the IoT ecosystem is made up of "smart" devices that gather, share, and analyze data using embedded systems such as sensors, chipsets, and communication hardware.
IoT devices send the data through an IoT gateway. These processes are often automated, requiring no human involvement. That said, people can still interact with the devices or access the data.
IoT can also leverage artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to collect data faster and make processes more dynamic.
What are the IoT Applications
There are various IoT applications across all industries including healthcare, manufacturing, transportation, and consumer retail. Most notably, the IoT gave rise to smart homes and buildings as well as industrial automation. Hospitals and healthcare facilities in Singapore are also starting to adopt IoT in their environment.
IoT applications in Singapore help industries simplify, automate, and control processes with speed and accuracy. Since IoT has many notable applications, new business models and revenue streams can be built as they allow businesses to create real-time data to develop new products and services.
For example, data collected by IoT devices helps businesses analyze big data with quick speed and accuracy. This quick analysis of data can help businesses improve services and products at a quick pace as compared to manually collecting and analyzing them, which could take years to accomplish.
Another example is how wearable health-tracking devices can keep track of patients’ heart rates remotely and the data can be analyzed in real-time. This enables doctors to detect irregularities and monitor a patient so they can provide the patients with the needed care as soon as symptoms show up.
IoT Components
There are five distinct components in IoT:
- Devices or Sensors – The devices are fitted with sensors and actuators to collect data from the environment to give to the gateway. Meanwhile, actuators perform the action (as directed after processing of data).
- Gateway – The collected data from the devices and sensors are then sent to the gateway and some pre-processing of data is done. The gateway also acts as a level of security for the network and transmitted data.
- Cloud – The collected data are then uploaded to the cloud, which is a set of servers connected to the internet.
- Analytics – After being received by the cloud, various algorithms are applied to the data for proper analysis of data
- User Interface – User can monitor and control the data in this final component.
Major Components of IoT
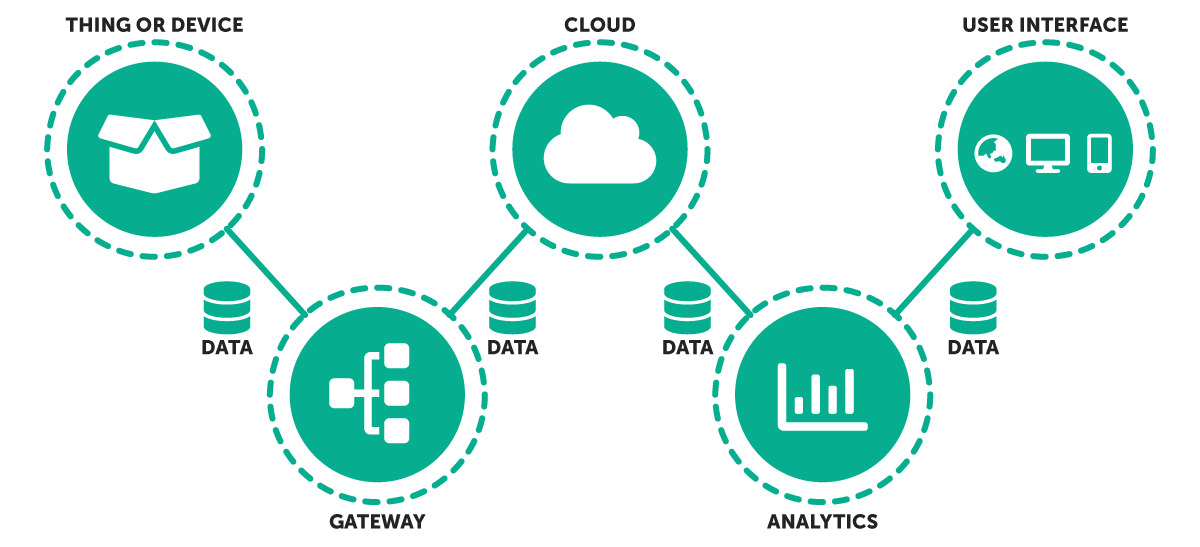
Image source: RF Page https://www.rfpage.com/what-are-the-major-components-of-internet-of-things/)
IoT Devices
IoT Devices Examples
There are several top IoT devices in the market, such as:
- Smart Mobiles
- Smart refrigerators
- Smartwatches
- Smart fire alarms
- Smart door locks
- Smart bicycles
- Medical sensors
- Fitness trackers
- Smart security systems and others
IoT for Security
Why Privacy and Security is Important in IoT
The number of linked IoT devices around the world has increased exponentially in recent years. By 2030, an estimated 50 billion IoT devices will be in use worldwide. As more device makers join the IoT ecosystem, it is important to note that security must not remain an afterthought. Without proper security put in place, hackers can easily gain access to personal data and seize the object’s functionality.
What are the Biggest IoT Security Risks and Challenges?
- Poorly secured smart devices – They may compromise sensitive data. Moreover, attackers can target critical information structure.
- Lack of encryption and access controls – without encryption and access controls put in place, there is a big potential for a breach or compromised data.
- Lack of device management – unmonitored and improperly managed IoT devices can prevent organizations from detecting an immediate threat. When a device is compromised or tampered with, the effects are irreversible.
- Weak passwords – inconsistent management of passwords may give hackers the upper hand to compromise an entire business network. If one employee does not adhere to the security policy, password-oriented attacks increase. Since devices are interconnected, one compromised device may cause a domino effect.
How to Improve IoT Security
As part of its efforts to strengthen IoT security, boost overall cyber hygiene standards, and better safeguard Singapore's cyberspace, the Cyber Security Agency of Singapore (CSA), a national cybersecurity organization, has introduced the Cybersecurity Labelling Scheme (CLS) for consumer smart devices.
The CLS is the region's first of its sort in Asia-Pacific. Smart gadgets will be graded based on their cybersecurity provisions under the plan. This will allow consumers to discover items with stronger cybersecurity features and make more educated purchasing decisions.
Security for IoT Devices
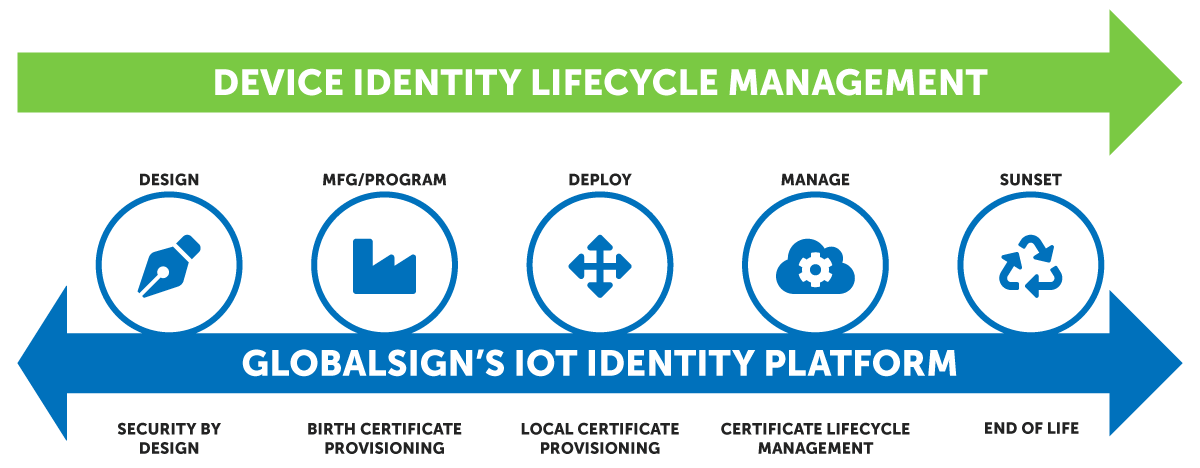
Providing software protection is one of the main ways to secure IoT devices. Ensuring the security of device identity for connected devices through a strong IoT identity platform is a must.
To successfully manage IoT devices, organizations must develop unique strong device identities to account for all potential breaches.
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)-enabled strong device identification can allow the principles of IoT security:
- Authentication
- Encryption
- Integrity
GlobalSign IoT Solutions
Here are some solutions that can be applied within the business landscape of all industries leveraging the benefits of IoT devices:
GlobalSign’s IoT Identity Platform is the perfect solution for managing IoT device identity. It taps on the power of PKI backed by digital certificates with these innovative products:
- IoT CA Direct – helps operate and secure device identity lifecycle management program through a trusted, cloud-based commercial certificate authority (CA).
- IoT Edge Enroll – ensures secure device enrollment and provisions unique, strong, and secure device identities.
The IoT Identity Platform enables IoT Device Identity Lifecycle Management. Organizations can secure and manage their IoT device identities, from certificate issuance to renewals and revocations.
We also have our IoT Developer Program for IoT developers and organizations looking for top-level technology to streamline and secure device identities. The IoT Developer Program and Portal provides a centralized platform where developers can access all the tools required to successfully integrate device identity provisioning.
Organizations can also make devices stronger and more secure by collaborating and partnering with the GlobalSign IoT Solutions Group, a trusted IoT security partner for device identities, through the IoT Partner Program.
Here’s all you need to know about our IoT security solutions and how they can meet the needs of businesses of all sizes.
Fighting and monitoring cybersecurity threats and IoT-related challenges to your company is essential for business continuity and security, but the process is incredibly difficult and time-consuming. A robust security solution is what most companies today need. A cybersecurity solution by GlobalSign is geared towards providing and securing device identities for IoT devices.
GlobalSign has a PKI-based cloud IoT Identity Platform designed for flexible, adaptable, and extensible IoT security. PKI provides a trustworthy IoT experience that is backed up by secure digital certificates issued by a reputable Certificate Authority (CA). You can request for a demo with us today to see how this solution can work for your business or you can speak with us to learn more about our IoT Device Security solution.