GlobalSign: A Pioneer in Digital Trust Since 1996
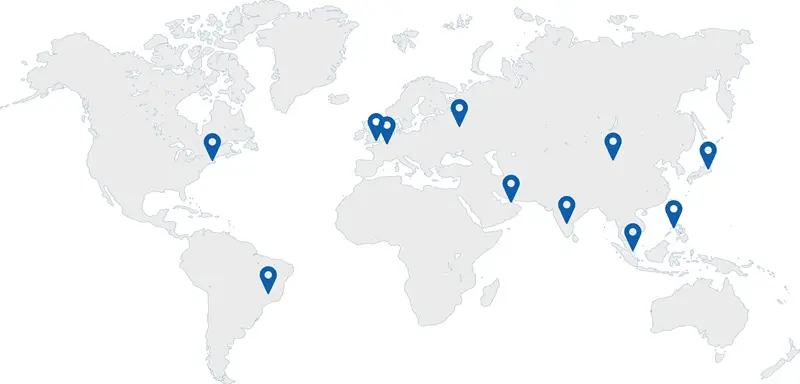
Choosing the right partner for your digital security needs is non-negotiable. At GlobalSign, we don't just offer solutions; we provide a legacy of trust built over 25+ years as a pioneering Certificate and Identity Authority.
Today, we invite you to explore the exceptional value GlobalSign brings to the table, redefining what it means to secure your enterprise in the digital age.