Digital signatures are a type of electronic signature that provide a high level of security and trust for online transactions. They are based on Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), which uses cryptographic keys to verify the identity and authenticity of the signer and the document. In this article, we will be answering some of your most common questions when it comes to digital signatures, what they are, and how they can be used for you.
What is a Digital Signature?
A digital signature is an electronic, encrypted, stamp of authentication on digital information such as email messages, macros, or electronic documents. A signature confirms that the information originated from the signer and has not been altered. A digital signature is created by applying a mathematical algorithm to the data and the signer’s private key, which is known only to the signer. The result is a unique string of bits, called the signature. The signature is then attached to the data or sent along with it.
What is the Difference Between a Digital and Electronic Signature?
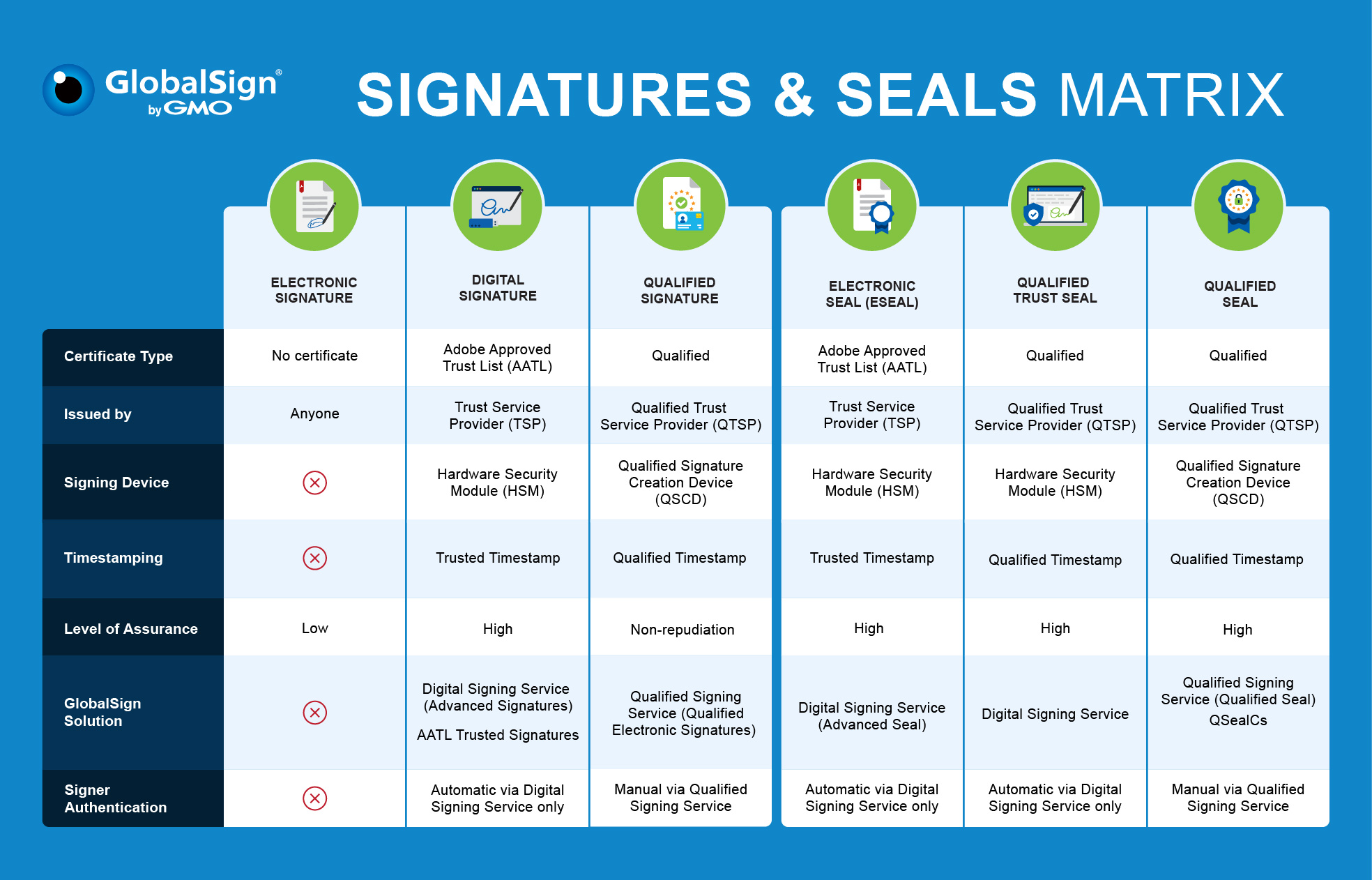
A digital signature and an electronic signature are both ways of signing a digital document or message, but the core difference is in their levels of security and validity. An electronic signature is a broad term that can refer to any symbol, image, or process that indicates the signer’s identity and consent. An electronic signature can be as simple as ticking a box or adding a scanned signature to a PDF document. An electronic signature is mostly used to verify a document, but it does not provide any encryption or protection against tampering.
A digital signature, on the other hand, is a specific type of electronic signature that uses public key cryptography to secure and authenticate the document or message. A digital signature involves applying a cryptographic algorithm to the data and the signer’s private key, which is known only to the signer, to generate a signature. The recipient can use the signer’s public key, which is embedded in a digital certificate, to verify the validity of the signature, the integrity of the data, and the authenticity of the signer. A digital signature provides authentication, trusted assurance, and time-stamping features that make it more reliable and secure than an electronic signature.
Are Digital Signatures Legal?
Yes, digital signatures are broadly considered accepted in court. However, the legal weight of digital signatures depends on their exact nature and local regulations. Only qualified signatures uniquely tied to the identity of the signer are considered indisputable and thus legally enforceable. Qualified signatures are granted the same legal status as handwritten signatures under various laws and regulations, such as Europe’s eIDAS regulation. This means that digital signatures can be used to execute documents and transactions, and can be used as evidence in court, as long as they meet certain requirements and standards. Some of these requirements and standards include:
- The signatory must have the intention to sign and consent to the document or transaction
- The signatory must have a unique and verifiable digital identity, which is linked to a digital certificate and a private key
- The signature must be created using a secure and reliable method, such as public key cryptography using SSL/TLS encryption, and must be attached to or associated with the signed data
- The signature must be capable of identifying any changes or tampering with the signed data, and must provide a tamper-evident seal
- The signature must comply with any specific formalities or conditions that apply to the type and purpose of the document or transaction, such as the need for witnesses, notarization, or registration
Digital signatures offer many benefits for legal and business purposes, such as enhancing security, trust, and efficiency, reducing costs and risks, and facilitating cross-border transactions and e-government services. However, it’s important to note digital signatures are not universally accepted or required for all types of documents and transactions, and there may be some exceptions or limitations depending on the jurisdiction, industry, or context.
Why Use Digital Signatures?
Digital signatures offer many benefits for online transactions, such as:
- Security: Digital signatures use encryption and hashing algorithms to protect the data from tampering and forgery. In the case of more advance signatures, like Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES), they also provide non-repudiation (based on the type of digital signatures used, in this case, Qualified Electronic Signatures) , which means that the signer cannot deny having signed the document
- Scalability: Digital signatures are a much easier, simpler and more efficient way of signing documents, which makes them ideal for use at a large scale. Digital signatures are flexible, and can maintain performance at different levels of use, all while being hosted on the cloud so it can be used freely by anyone with permission.
- Trust: Digital signatures are based on PKI, which establishes a chain of trust between the signer, the Certificate Authority (CA), and the recipient. The recipient can verify the validity of the signature and the certificate using the public key of a CA, which is widely recognized and trusted by browsers, operating systems, and devices
- Efficiency: Digital signatures enable faster and easier signing of documents, without the need for paper, ink, or physical delivery. They also reduce the costs and risks associated with manual processes, such as errors, delays, or fraud
- Compliance: Digital signatures comply with various legal and regulatory frameworks, such as the eIDAS regulation in the European Union, the ESIGN Act in the United States, and the ETSI standards. They also meet the requirements of various industries, such as finance, healthcare, and government
How to Create and Use Digital Signatures?
To create and use digital signatures, you need to follow a few steps.
How to Obtain a Digital Certificate
You can request a digital certificate from a CA, such as GlobalSign, by providing some information about yourself or your organization. The CA will verify your identity and issue you a digital certificate that contains your public key and other details.
How to Digitally Sign a Document
You can use a software or a service that supports digital signatures, such as DocuSign, to sign a document electronically. The software will use your private key, which is securely stored by you, to create a digital signature that is attached to the document. The signature will also include a timestamp and a hash of the document, which are used to ensure the validity and integrity of the signature and the document.
How to View a Digital Signature
You can send and receive a document that has a digital signature via email or other online platforms. The recipient can verify the signature and the certificate using a public key, which is available online or embedded into the document. The verification will confirm the identity of the signer, the authenticity of the document, and the status of the certificate. Recipients do not need any additional software to verify the authenticity of the document, and signed documents can be opened in the recipient’s regular software such as Adobe Reader or Microsoft Word.
How to Manage and Maintain Digital Signatures?
Managing and maintaining digital signatures is crucial for ensuring the integrity and legality of electronic documents, and to do so you should be keeping in mind to check you’re doing the following tasks:
- Monitor and Update Certificates: You need to monitor the expiration dates and the validity of your certificates, and renew them before they expire. You also need to update your certificates if there are any changes in your identity or your organization.
- Establish Policies and Procedures: To effectively manage digital signatures, organizations must establish clear policies and procedures. These should outline the acceptable use of digital signatures, define the roles and responsibilities of signatories, and set forth the processes for signature creation and verification. Training should be provided to all employees to ensure they understand the legal significance of digital signatures and adhere to the established guidelines.
- Use Trusted Digital Signature Solutions: Choosing the right digital signature solution is paramount. Organizations should opt for trusted providers that offer solutions compliant with international standards, such as the eIDAS in the EU, and the ESIGN Act in the United States. GlobalSign has a proven track record of reliability and security that establishes it as a leading trusted provider of Digital Signing Services (DSS) and other signing solutions.
- Secure Key Management: The security of digital signatures hinges on the secure management of cryptographic keys. Organizations must implement stringent key management practices, including secure key generation, storage, and disposal methods. Access to private keys should be restricted to authorized individuals, and the use of hardware security modules (HSMs) for key storage provide an additional layer of security.
- Maintain Audit Trails: Audit trails are essential for tracking the use of digital signatures and verifying their validity over time. An effective audit trail would involve the use of a timestamp that records the date and time of signature, the identity of the signatory, and the document’s integrity at the time of signing. This information should be securely stored and protected against unauthorized access or tampering, ensuring it can serve as legal evidence if required.
- Revoke and Replace Certificates: You need to revoke your certificates if they are compromised, lost, or stolen, and replace them with new ones. You also need to inform the CA and the recipients of the revocation and the replacement of your certificates.
- Audit and Report on Certificates: You need to audit and report on the usage and the status of your certificates, and comply with the policies and the standards of the CA and the industry. You also need to keep track of the documents that you have signed and received, and the signatures that you have verified.
Digital signatures represent a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity, offering businesses unparalleled assurance in the authenticity and integrity of their digital communications. At GlobalSign, we understand the critical role digital signatures play in streamlining operations, enhancing security, and building trust in digital transactions. Digital signatures extend beyond simple convenience; they are a testament to a company’s commitment to protecting stakeholders’ data and upholding stringent security standards.
While this FAQ aims to address common inquiries, we recognize that the landscape of digital security is ever-evolving and complex. Therefore, we invite you to reach out to our dedicated team of experts for any further questions or personalized advice. Our specialists are equipped with the latest knowledge and are eager to assist you in navigating the intricacies of digital signatures and how they can fortify your business’s digital infrastructure.
Remember, in the digital age, your signature is a statement of security and reliability. Let us help you make that statement with confidence.
Contact our experts today to learn more about document signing solutions







